What is the relative importance of phytoplankton and attached macroalgae and epiphytes to food webs on offshore oil platforms?
Abstract
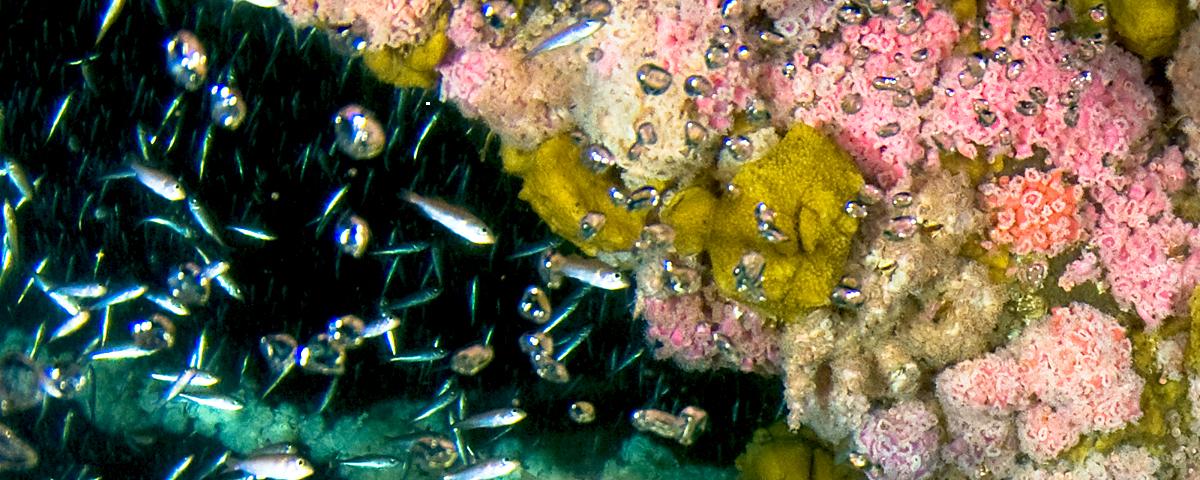
Offshore oil platforms function as artificial reefs, but little is known about the food webs that fuel platform-dwelling biota. Here, we use carbon and nitrogen isotopes in tissues of biota from two offshore oil platforms to estimate the importance of phytoplankton and platform-associated macroalgae and epiphytic microalgae to the diets of platform-dwelling consumers. Although the consumption of macroalgae was indicated for small, mobile consumers including crabs, amphipods, and harpacticoid copepods, both a Bayesian mixing model and temporal changes in isotope composition identified phytoplankton as the most important basal resource for these consumers. Sessile suspension-feeding barnacles and oysters consumed phytoplankton and epiphytes, and probably redirected large amounts of pelagic production to other consumers. Secondary consumers including syllid polychaetes and the blennies, Molly Miller Scartella cristata and Tessellated Blenny Hypsoblennius invemar, exhibited a distinct contribution from epiphytes although large ranges in all potential basal resources were observed. Elemental and isotope analysis of the gut contents of individuals indicated that the nektonic Gray Triggerfish Balistes capriscus was omnivorous, directly consuming reef-derived macroalgae and epiphytes as well as animal tissue. Although we found that reef-derived resources entered benthic and nektonic food webs surrounding platforms, phytoplankton was the dominant basal resource fueling platform-dwelling communities at the time of our study, and no consumer studied specialized on a diet of red macroalgae. If these findings are generally representative, platform-derived benthic algae would not be integral to food-web function on artificial reefs, and reef function should be similar in areas both favorable to and unfavorable to in situ algal growth.