Modeling fish production for southern California’s petroleum platforms
Abstract
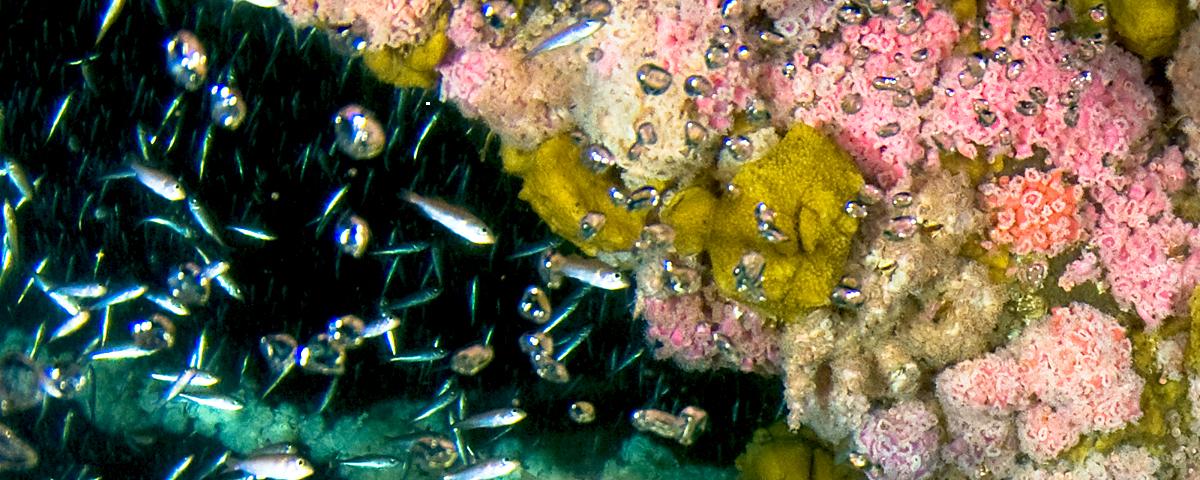
California's oil platforms are nearing the end of their productive lives and therefore will be decommissioned in the near future. These structures have been shown to be important habitats for both settlement and growth for reef fishes. Important information on the biological effects (i.e., loss of biomass and production) of different decommissioning options has not yet been explored in detail. An important step in the assessment of these different decommissioning options is to look at the potential loss of fish production and habitat under the different alternatives. Using the large amount of information available on fish abundances at these structures, we have created a model to estimate the standing stock of fishes and production that would be lost because of both partial (removal from surface to 85 ft) and complete removal (the 2 decommissioning options being considered). Complete removal of a platform will likely eliminate most of its fish biomass; however, this study has shown that for rockfishes, which settle predominantly below 85 feet (26 m) and move deeper as they age, partial removal through topping would leave more than 90% of the fish biomass at the deeper platforms. Modeling of larval dispersal suggests that platforms provide an important opportunity for recruitment of fish larvae and that many larvae produced near the platforms would settle elsewhere in the region. The results presented here indicate that, even if topped, the potential contribution of platform habitat to biological resources (e.g., fish production) in this region is significant.