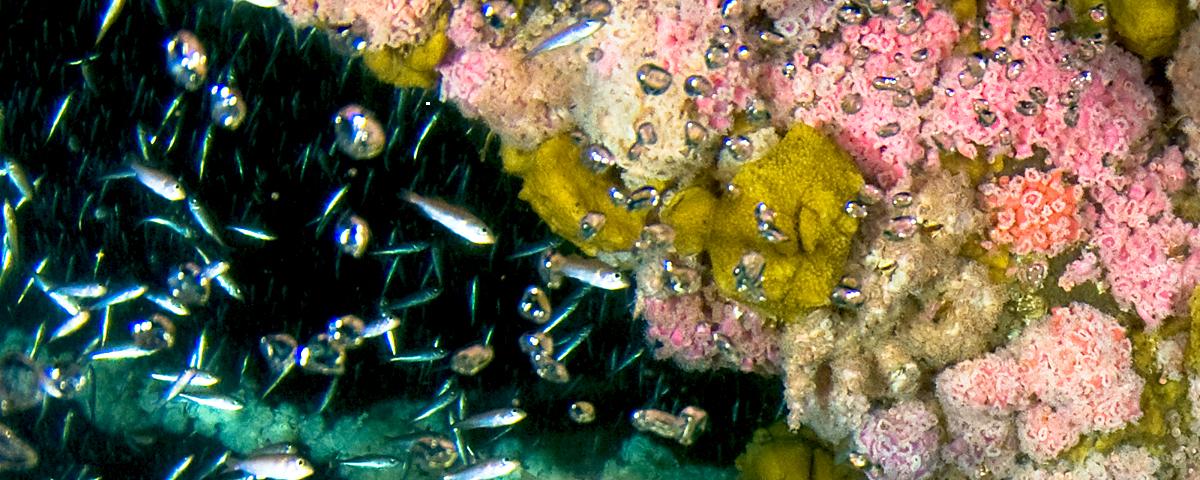
Benthic biology
Abstract
Samples for this program were collected at 20 platforms and four control sites located on the Louisiana OCS. These sites are contained in a roughly rectangular area lying west of the Mississippi Delta and extending from 5 km (3 miles) to 120 km (75 miles) offshore and about 320 km (200 miles) west. Meiofauna, macroinfauna, macroepifauna and demersal fish were collected during three sampling cruises : Cruise I-May 20 to June 2, 1978; Cruise 11- A-August 21 to September 5, II-B-August 21 to September 6, II-C-September 17 to 24; and Cruise III-January 6 to 15, 1979. Four Primary Platforms and four Control Sites were sampled during each cruise. During Cruise II, an additional 16 Secondary Platforms (hereafter denoted as Secondary Sites SS-S20) were sampled.
From the Conclusions: “The benthic fauna of the Louisiana continental shelf is stressed, as indicated by the large number of opportunistic species and the pronounced dominance of some taxa. Natural environmental perturbations, namely tropical cyclones and flooding by the Mississippi River, contribute to this stress . Approximately once every four years, a tropical cyclone directly hits the coast of Louisiana. Annually, the effects of one or more cyclones can be felt on the shelf. Every 3 .6 years the Mississippi River floods its banks or natural levees . The offshore effects of leveeing of the Mississippi were probably first noticed in 1885 and reached a peak after 1927. It may take over two years for an area to return to normal after a tropical cyclone and at least a year for it to recover from hypoxic bottom conditions . Because of the time period necessary for recovery and the periodic nature of "normal" perturbations on the Louisiana shelf, the fauna probably remains in a depressed state as compared with a similar fauna offshore Texas.
The fauna encountered in this study closely resembles that found offshore Texas. As the fauna approaches Port Isabel it assumes certain tropical components. Much of the fauna on the Louisiana shelf also resembles that of the eastern United States as far north as Cape Cod, Massachusetts. There is substantial evidence that the Carolinian province extends along the Louisiana coast, forms part of the Northwestern Gulf Provincand contains four reported assemblage groupsinner shelf, intermediate shelf, outer shelf, and pro-delta.Meiofauna and macroinfauna diversities were higher at the Primary Sites than at the Control Sites, probably because the Primary Sites provided more and different microhabitats. Correlation analysis indicated that distance from the mouth of the Mississippi River, depth, temperature, salinity, D.O., percent sand, percent silt, T.O.C., and the presence of hypoxic bottom conditions were significantly correlated with species diversity, evenness, and number of individuals of selected taxa or taxa groups. Ethane, propane, total unsaturated hydrocarbonsthe contamination index, chromium, lead, cadmium, copper, nickel, iron, and zinc were also found to be significantly correlated with selected biotic variables. Level of impact of the significant abiotic variables cannot be determined at this time. This information should be available through regression analysis. However, the independent variable data set used for regression in this program contained considerable multicollinearity and the results could not be usd to produce predictive equations. Further refinement of the regression equations was not considered to be within the scope of this study.
Hydrocarbon and trace metals analyses indicate that the study area suffers from sub-lethal chronic exposure to hydrocarbons and trace metals. Any effects from drill cuttings or drilling fluids were restricted to within less than 500 m of a platform . Some of the contamination has its input from the Mississippi River, but some of the contamination appears to be platform derive. The benthic fauna of the Louisiana continental shelf is indeed stressed over much of the area by natural environmental perturbations and locally by petroleum production activities . Several indicator organisms were identified in this project and can be very useful in future monitoring. However, it is extremely important that these indicators, that is, their presence or absence, be evaluated within the context of the entire community. The health of the community should be determined based upon as much information as possible and not on limited knowledge.”