The Artificial Reef Studies
Abstract
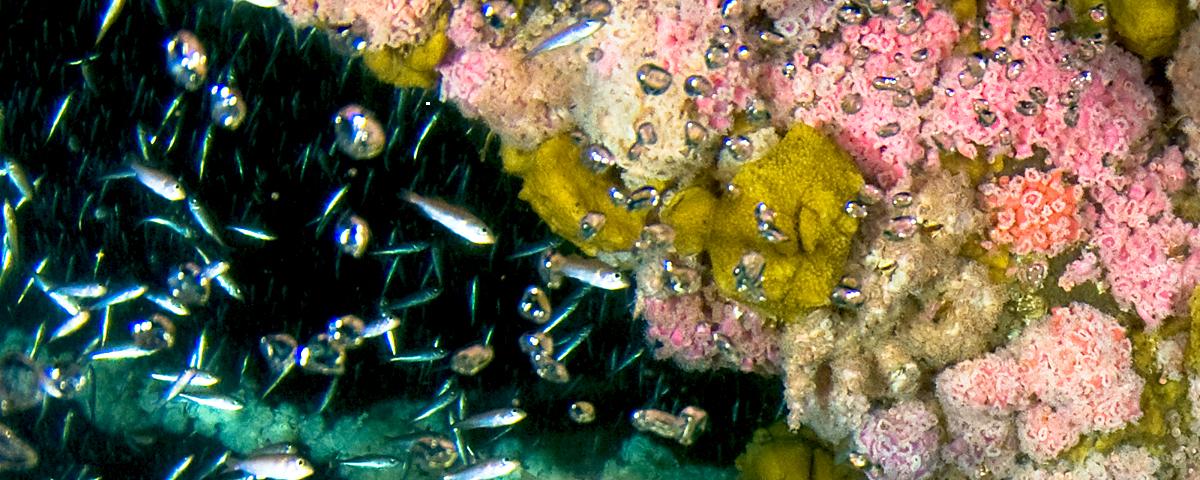
Surveys of biofouling macroepibiota and fishes were made in June 1978 at four production platforms offshore Louisiana and were supplemented by limited observations made at an additional 15 platforms in August and September of 1978. Biofouling communities of nearshore platforms were dominated by barnacles in terms of biomass, whereas the communities on offshore platforms were dominated by bivalves. Primary production was largely restrictedto surface zones of nearshore platforms but at some offshore platforms primary producers were abundant to depths of 30 m.
Platform habitats offshore Louisiana were classified into three zones using depth and faunal characteristics---Coastal (shore to 27-m bottom contour), Offshore (37 to 64 m) and Blue Water (> 64 m). A transitional area between the Coastal and Offshore Zones was considered to have been represented between the 27- and 37-m depth contours. Platforms in the Coastal Zone were dominated by barnacles and shorefishes. Bivalves and shorefishes were abundant at platforms in the Offshore Zone but were supplemented by a rich Caribbean fauna. The Caribbean fauna was dominant at platforms in the Blue Water Zone.
Taxonomic findings of significance include documentation of the presence of four species of oysters (Crassotrea virginica, Ostrea equestris, Lopha frons, and Hyotissa thomasi) on Louisiana platforms and the occurrence of two other bivalves (Pinna carnea, Kellia suborbicularis) new to the area. Species represented on production platforms that had formerly been recorded only from natural banks of the northern Gulf included the sea urchin, Eucidaris tribuloides, and the spiny lobster, Panulirus sp.
Results of this study, as well as those from many previous studies, document that structures concentrate large numbers of epibiota and fishes which would not be as abundantly represented in the same area in the absence of structures. In contrast to some previous studies, produced water discharges were observed to have a detrimental effect on platform macroepibiota. The magnitude and significance of this effect have yet to be well defined.